Paul Rutherford explains how reason, Christ’s resurrection, and the Bible all testify that Jesus is the only way to heaven.
 I can’t drive around town seven days straight without passing at least one car with a bumper sticker that reads, “Coexist” on the back. You know the one. It spells the word using symbols associated with the world’s faiths, ancient and modern.
I can’t drive around town seven days straight without passing at least one car with a bumper sticker that reads, “Coexist” on the back. You know the one. It spells the word using symbols associated with the world’s faiths, ancient and modern.
The popularly held mantra is that “all religions are equally valid ways to heaven.” This is what’s called pluralism. So is there room in this brave new world for the words of an ancient and historically respected faith?
Jesus once said, “I am the way, and the truth, and the life. No one comes to the Father except through me.” (John 14:6) That sounds offensive and inflammatory today. I will remind you that Jesus said it, not me.
Even more important is the truth question. It is perhaps even more offensive! Are Jesus’ words true?
I fully acknowledge even the question itself may strike you as antiquated, out of date. Perhaps I sound to you like an eccentric, soured-up, fuddy-duddy. I may be. But if the words of Jesus are true, then far more than your offended sense of style is at stake here. Far, far more.
So listen up. And take note because this crazy sounding first-century Jewish rabbi made some crazy-big statements about the nature of man, the nature of reality, and how to live the good life, here, now, and forever. Does that at least sound appealing to you? If even just for the sake of a little controversy?
Explore with me the words of this rabbi. In this article we’ll think through three reasons you should agree with him. And maybe you’ll even find eternal life in the process. If you’re a long-time listener to Probe radio, or a regular listener, this may sound familiar. I have another program exploring the position that Jesus is the only way to God. This one is part two. In this one I give you three reasons Jesus is in fact the only way to heaven. In the previous program, I defended Jesus’ statement against three lines of criticism. So in the next sections I’ll explain how reason, the resurrection, and the Word all testify that Jesus is the only way to heaven.
Jesus the Only Way Because of Reason
Western culture today is more pluralistic and secular than ever before. This means at least in one small part, that people believe multiple religions lead to heaven. Western culture has been moving this way for some decades. Now it has reached mainstream. Pop culture increasingly accepts this. It is therefore so much more important to consider this exclusive claim Jesus made. He said, “I am the way, the truth, and the life. No one comes to the Father except by me.” (John 14:6)
This is an increasingly unpopular teaching. Before I defend it, allow me to clarify. It was made by the Lord Jesus himself. I didn’t make it up. I am merely defending it.
So today I want to talk about how it is reasonable to believe this statement—why it is that you should yourself believe Jesus is the only way to heaven.
Today’s reason is logic itself. I will base this conclusion on two points: first, that the belief in one God is more logically defensible than believing in multiple creator gods; and second, that the belief in Jesus Christ as God is more reasonable than claims to deity made by others.
The first point is that believing in one creator God is more reasonable than believing in multiple. The god Aristotle believed in (the unmoved mover) was eternally simple. That is, at the root of all things is ultimately one thing—one cause, one source, one origin to which all other things owe their existence.{1} This position beautifully avoids the difficulty of what philosophers call reductio ad absurdum—or the problem of infinite regression—or the problem of which came first, the chicken or the egg? The search for the first, original, or ultimate source, does not continue on and on forever. It cannot.
The second point is that Jesus is the most reasonable candidate for divinity. I respect the Buddha. But he never claimed to be God. Neither did Mohammad. Jesus was very clear. He claimed to be God.
Consider His teachings. They have not been surpassed in excellence in the two millennia that have passed since He walked the earth. Consider His actions. History’s best biographies about the man Jesus, record Him loving His enemies, healing the sick, and showing compassion to outcasts. Jesus’ life exemplified extraordinary moral rectitude.
I conclude, therefore, that it is more reasonable to believe Jesus is the only way to God given that it is more reasonable to believe in only one creator God, and given that Jesus has the best case for divinity among man’s founders of faith.
Jesus the Only Way Because of the Resurrection
We have a saying in American culture that nothing is certain but death and taxes. So if the taxman doesn’t come to call, the grim reaper will eventually. Death finds each of us, so we must face our own mortality.
By the best historical accounts Jesus also died and was buried, just like so many of His human brothers before Him.{2} But Jesus, on the other hand, experienced something unique, declaring Him God above all others.
I speak, of course, of resurrection.{3} Jesus Christ is the only person ever to have raised up Himself from the dead of his own volition, and by His own power.
This one point may be the most compelling of the three I offer this week. It is perhaps the most intuitive case for Jesus being the only way to Heaven. If Jesus really died and raised Himself from the dead, then His power exceeds those of any other man before Him, or after, for
that matter. Surely He must be God.
No other religious figure can make that claim. In a class by Himself, Jesus reigns over all the founders of world religions. Muhammad’s burial site is a common tourist destination in Saudi Arabia for contemporary pilgrims. Buddha’s cremation site is in northern India. No such site exists today in contemporary Israel for Jesus. His body has no confirmed remains.
The tomb is empty. That much is clear. Records indicate He definitely died and was buried. The empty tomb demands an explanation. Resurrection makes the most sense. Jesus is the only way because He is the only one who has died and raised himself up to new life.
We have several excellent articles at our website devoted to just this topic.{4} Go check them out for more detail. Jesus is who He said he is, “The way, the truth, and the life.” (John 14:6) So the question is, do you want some? Believe in Jesus today by faith.
Jesus the Only Way Because the Word Declares It
Western culture today increasingly accepts the belief that multiple religions are equally valid and they are all ways to eternal life. I propose to you today another reason to believe something
diametrically opposed to this—namely that the Jesus Christ revealed in the Bible, is the only way to eternal life. As the gospel writer John quoted Him, He is, the way, the truth, and the life (14:6). No one comes to the Father except through Him.
This third and final line of reasoning that Jesus is the only way to eternal life, springs from the Bible—from the very word of God itself.
You may not accept the Bible as God’s word. That’s ok. Just hear me out. Let me explain how this line of reasoning at least makes sense. Then after you’ve heard it, you can judge for yourself if it’s true or not.
So first, the Bible claims to be God’s word (2 Timothy 3:16). If we therefore assume the very commonly held conception that God is good and perfect, then that includes the words He speaks as well. So if He speaks good words, then those words must be true. They must accurately describe reality.
The Bible also makes this claim. Jesus in a famous prayer to the Father asks him to sanctify His disciples with the truth before stating, “Your word is truth.” (John 17:17) It’s a profound statement.
So if God’s word is true, and God says in His word that Jesus is, in fact, the only way to God—that none can come to Him except by Jesus, then that means it’s true. See how simple that is?
But this statement is also made in another part of the Bible, Acts 4:12. Peter and John have been arrested and are being examined by the Jewish leaders. Peter declares Jesus to them and explains, “There is no other name under heaven, given among men, by which we must be saved.”
I fully admit this line of reasoning rests on you acknowledging the authority of the Bible—in which case you may not have needed to be convinced in the first place. But if you had not already been convinced of the truth of God’s word, I am very sincerely relying on the power of the Spirit at work in you to believe this truth. (Isaiah 55:11)
Conclusion
In this article we considered the truth of a controversial claim. It might be one of the most hotly contested claims in religion today—that Jesus Christ is the only way to heaven.
This is not popular these days in America, Europe, anywhere in the English speaking West, or the non-English speaking West. To hear responses to criticisms against the claim, check out part one of this two part series.
Jesus was Himself no stranger to controversy. He died a criminal’s death at the hands of His enemies. He was killed and buried. The Jewish and Roman leaders were smugly satisfied they’d dispatched this unquiet voice.
But when Jesus’ enemies attempt to end his earthly ministry, they unknowingly ushered in a spiritually unending ministry of atonement and reconciliation. By his death Jesus paid the price of sin—death—satisfying the just wrath of God. Jesus made peace with God on your
behalf. Believe in Him by faith today and you can have peace with God. Would you like to have peace with him? Tell Him right now. Use your voice or pray silently. But tell Him. Go ahead.
The only thing required of you to receive eternal life is to believe Jesus is Lord. One of Jesus’ most famous sayings is, “For God so loved the world, that he gave his only Son, that whoever believes in him should not perish but have eternal life.” (John 3:16)
Confess this belief with your mouth that Jesus Christ is God and believe in your heart that God has raised up his Son from the dead. And you can be saved. (Romans 10:9)
Jesus is the only way to God because there is no other way to get to God but by Jesus. Mankind is imperfect. You are dead in your transgressions and sins. The only way to satisfy God’s holy wrath is to give Him what is due: death. Jesus died that death for you. He’s the only one who could ever have paid your debt. And He did.
Human reason leads us to this beautiful conclusion that Jesus is the only way. God has declared it himself clearly in his divinely inspired book—the Bible. His resurrection seals it.
If you believed this for the first time today you are now heir to an eternal throne. Pick up a Bible and read Jesus’ life story in the book of John. Tell a friend who’s a Christian. Make plans to join them at their church Sunday. Keep praying and reading the Bible. You can discover the wonderful adventure of life in Jesus Christ, the only way to God.
Notes
1. Metaphysics, Lambda.
2. Matthew 27; Mark 15; Luke 23; John 19
3. Matthew 28; Mark 16; Luke 24; John 20
4. Jesus’ Resurrection: Fact or Fiction? — A Clear Christian Perspective;
What Difference Does the Resurrection Make?;
The Resurrection: Fact or Fiction?
— A Real Historical Event;
The Answer Is the Resurrection
©2020 Probe Ministries

 Some skeptics claim that no one claimed that Jesus was not seen as divine until the council of Nicaea. In 2003 this view was popularized in Dan Brown’s novel, The Da Vinci Code and in the movie that followed. In this novel Brown uses a fictional story to make factual claims about the origin of Christianity and the person of Jesus. While investigating a murder, several of Brown’s characters make some disturbing discoveries. One character states, “Jesus was viewed by His followers as a mortal prophet…A great and powerful man, but a man nonetheless.”
Some skeptics claim that no one claimed that Jesus was not seen as divine until the council of Nicaea. In 2003 this view was popularized in Dan Brown’s novel, The Da Vinci Code and in the movie that followed. In this novel Brown uses a fictional story to make factual claims about the origin of Christianity and the person of Jesus. While investigating a murder, several of Brown’s characters make some disturbing discoveries. One character states, “Jesus was viewed by His followers as a mortal prophet…A great and powerful man, but a man nonetheless.” I was sitting in my car at a red light and I saw a bumper sticker on the car in front of me that said, “Coexist.” Only, the letters on the bumper sticker are religious symbols. A crescent stands in place of the letter “c,” a peace symbol in place of the letter “o,” and some of the other symbols included a cross, a Star of David, and a yin-yang, all used to create the word “coexist.”
I was sitting in my car at a red light and I saw a bumper sticker on the car in front of me that said, “Coexist.” Only, the letters on the bumper sticker are religious symbols. A crescent stands in place of the letter “c,” a peace symbol in place of the letter “o,” and some of the other symbols included a cross, a Star of David, and a yin-yang, all used to create the word “coexist.”

 CULTURE’S LIE: I can create my own reality. For example, recently a man abandoned his wife and seven children, announcing his chosen identity of a 6-year-old girl.
CULTURE’S LIE: I can create my own reality. For example, recently a man abandoned his wife and seven children, announcing his chosen identity of a 6-year-old girl.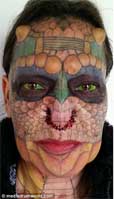 Another man, deciding his identity is a female dragon, cut off his ears and nose, dyed his eyes, and inserted horns in his forehead.
Another man, deciding his identity is a female dragon, cut off his ears and nose, dyed his eyes, and inserted horns in his forehead.