Kerby Anderson looks at the harmful effects of both legal and illegal gambling. He considers the negative impacts on society, government policy, and the economy when gambling is prevalent in a culture. From a Christian worldview perspective, he considers how gambling introduces problems such as covetousness, poor work ethics, and destroyed family units.
 This article is also available in Spanish.
This article is also available in Spanish.
Gambling used to be what a few unscrupulous people did with the aid of organized crime. But gambling fever now seems to affect nearly everyone as more and more states are legalizing various forms of it.
Thirty years ago, gambling was a relatively rare phenomenon with casinos operating only in the distant Nevada desert and a few states with lotteries or pari-mutuel betting. Today, legalized gambling is permitted in forty-seven states and the District of Columbia. More Americans are gambling than ever before, and they are also gambling more money.{1}
The momentum seems to be on the side of those who want legalized gambling as a way to supplement state revenues. But these states and their citizens often ignore the costs that are associated with legalized gambling.
Types of Gambling
Gambling comes in many forms. Perhaps the most popular type of gambling is state-sponsored lotteries. This would include the weekly lottery games, as well as the daily lottery numbers and scratch-off ticket games.
A second type of gambling would be casinos. Gambling in this venue would include jackpot slot machines, video card game machines, various casino card games such as poker and blackjack, and other casino games such as roulette.
Sports betting is a third type of gambling. Someone can bet on the outcome of a sporting event or a particular part of a sporting event. Usually, bets are placed on a bookmaker’s odds so that the actual bet is against the point spread. Sports betting would also include illegal office pools and even weekend golfers who bet dollars or cokes for each hole.
Pari-mutuel betting (horse racing, dog racing, and jai alai) is another form of sports gambling. Horse racing is legal in 43 states with over 150 racetracks in the United States.
Convenience gambling (also called retail gambling) includes stand-alone slot machines, video poker, video keno, and other games. These are usually found in bars, truck stops, and convenience stores.
Online gambling represents a new frontier in the spread of gambling. The availability and accessibility of Internet gambling appears to have greatly increased the number of people gambling on a regular basis.
Bad Social Policy
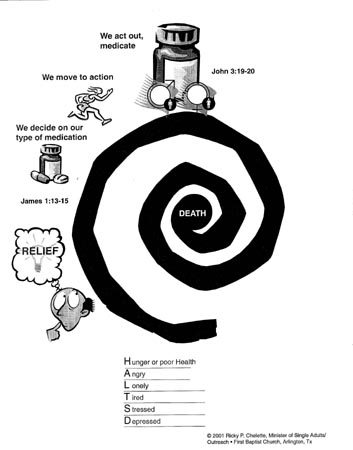
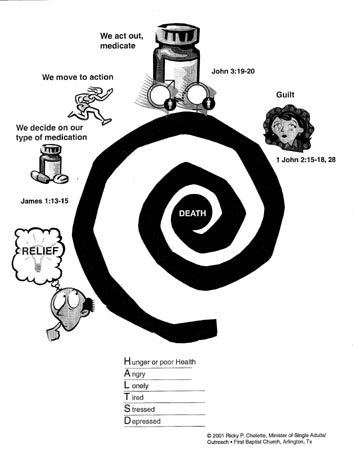
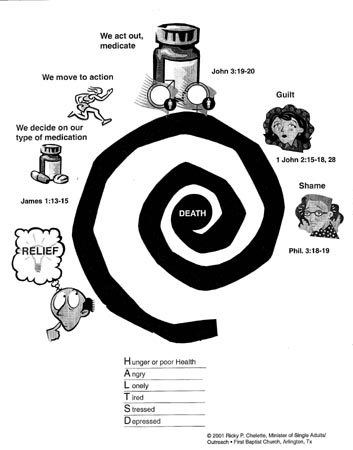
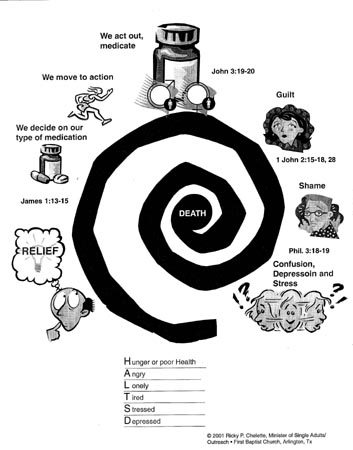
Legalized gambling is bad social policy. At a time when Gamblers Anonymous estimates that there are at least 12 million compulsive gamblers, it does not make a lot of sense to have the state promoting gambling. State sponsorship of gambling makes it harder, not easier, for the compulsive gambler to reform. Since about 96 percent of those gamblers began gambling before the age of fourteen,{2} we should be especially concerned about the message such a policy sends to young people.
The economic costs that gamblers themselves incur are significant. The average compulsive gambler has debts exceeding $80,000.{3} And this figure pales in comparison with other social costs that surface because of family neglect, embezzlement, theft, and involvement in organized crime. Compulsive gamblers affect the lives of family, friends, and business associates. Some of the consequences of gambling are marital disharmony, divorce, child abuse, substance abuse, and suicide attempts.
Proponents argue that state lotteries are an effective way to raise taxes painlessly. But the evidence shows that legalized gambling often hurts those who are poor and disadvantaged. A national task force on gambling found that those in the lowest income bracket lost more than three times as much money to gambling (as a percentage of income) as those at the wealthiest end of the spectrum.{4} One New York lottery agent reports that “seventy percent of those who buy my tickets are poor, black, or Hispanic.”{5} And a National Bureau of Economic Research “shows that the poor bet a much larger share of their income.”{6} The study also found that “the less education a person has, the more likely he is to play the lottery.”{7}
A major study on the effect of the California lottery came to the same conclusions. The Field Institute’s California poll found that 18 percent of the state’s adults bought 71 percent of the tickets. These heavy lottery players (who bought more than twenty tickets in the contest’s first forty-five days) are “more likely than others to be black, poorer and less educated than the average Californian.”{8}
Studies also indicate that gambling increases when economic times are uncertain and people are concerned about their future. Joseph Dunn, director of the National Council on Compulsive Gambling, says, “People who are worried about the factory closing take a chance on making it big. Once they win anything, they’re hooked.”{9}
The social impact of gambling is often hidden from the citizens who decide to legalize gambling. But later these costs show up in the shattered lives of individuals and their families. One study in The Journal of Social Issues found that as gambling increases, there is an increase in “(a) proportion of divorce and separation; (b) disagreement about money matters with one’s spouse; (c) lack of understanding between marital partners; and (d) more reported problems among children of gamblers.”{10}
Psychologist Julian Taber warns, “No one knows the social costs of gambling or how many players will become addicted . . . the states are experimenting with the minds of the people on a massive scale.”{11} Families are torn apart by strife, divorce, and bankruptcy. Boydon Cole and Sidney Margolius in their book, When You Gamble—You Risk More Than Your Money, conclude, “There is no doubt of the destructive effect of gambling on the family life. The corrosive effects of gambling attack both the white-collar and blue-collar families with equal vigor.”{12}
The impact on crime is also significant. The crime rate in gambling communities is nearly double the national average.{13} Researchers calculate that for every dollar the state received in gambling revenues, it costs the state at least three dollars in increased social costs (for criminal justice and social welfare).{14}
Bad Governmental Policy
Legalized gambling is also bad governmental policy. Government should promote public virtue, not seduce its citizens to gamble in state-sponsored vice. Government is supposed to be servant of God according to Romans 13, but its moral stance is compromised when it enters into a gambling enterprise.
Citizens would be outraged if their state government began enticing its citizens to engage in potentially destructive behavior (such as taking drugs). But those same citizens see no contradiction when government legalizes and even promotes gambling. Instead of being a positive moral force in society, government contributes to the corruption of society.
Ross Wilhelm, professor of business economics at the University of Michigan, says,
State lotteries and gambling games are essentially a “rip-off” and widespread legalization of gambling is one of the worst changes in public policy to have occurred in recent years. . . . The viciousness of the state-run games is compounded beyond belief by the fact that state governments actively advertise and promote the games and winners.{15}
The corrosive effect legalized gambling has on government itself is also a cause for concern. As one editorial in New York Times noted, “Gambling is a business so rich, so fast, so powerful and perhaps inevitably so unsavory that it cannot help but undermine government.”{16}
Legal and Illegal Gambling
One of the standard clichés used by proponents of legalized gambling is that by instituting legal gambling, illegal gambling will be driven out. This argument makes a number of faulty assumptions. First, it assumes that people are going to gamble anyway; and so the state might as well get a piece of the action. Second, it assumes that given the choice, people would rather gamble in a state-sponsored program because it will be regulated. The state will make sure that the program is fair and that each participant has an equal chance of winning. Third, it assumes that if the state enters the gambling arena, it will drive out illegal gambling because it will be a more efficient competitor for gamblers’ dollars.
While the arguments seem sound, they are not. Although some people do gamble illegally, most citizens do not. Legalized gambling entices people to gamble who normally would not gamble at all. Duke University researchers have found that the lottery is a “powerful recruiting device” because one-fourth of those who otherwise would not gamble at all do bet on lotteries.{17}
Second, legal gambling does not drive out illegal gambling. If anything, just the opposite is true. As legalized gambling comes into a state, it provides additional momentum for illegal gambling. The Organized Crime Section of the Department of Justice found that “the rate of illegal gambling in those states which have some legalized form of gambling was three times as high as those states where there was not a legalized form of gambling.”{18} And one national review found that
In states with different numbers of games, participation rates increase steadily and sharply as the number of legal types of gambling increases. Social betting more than doubles from 35 percent in states with no legal games to 72 percent in states with three legal types; the illegal gambling rate more than doubles from nine percent to 22 percent; and commercial gambling increases by 43 percent, from 24 to 67 percent.{19}
Legalized gambling in various states has been a stimulator of illegal gambling, not a competitor to it.
The reasons for the growth of illegal gambling in areas where legalized gambling exists are simple. First, organized crime syndicates often use the free publicity of state lotteries and pari-mutuel betting to run their own numbers games. The state actually saves them money by providing publicity for events involving gambling. Second, many gamblers would rather bet illegally than legally. When they work with a bookie, they can bet on credit and do not have to report their winnings to the government, two things they cannot do if they bet on state-sponsored games. This explains why illegal gambling thrives in states with legalized gambling.
Another important issue is the corrupting influence legalized gambling can have on society. First, legalized gambling can have a very corrupting influence on state government. In the last few years there have been numerous news reports of corruption and fraud in state lotteries. Second, there is the corrupting influence on the citizens themselves. Gambling breeds greed. Research has shown that the number of compulsive gamblers increases between 100 and 550 percent when legalized gambling is brought into an area.{20} Every day, otherwise sane people bet large amounts of money in state lotteries because they hope they will win the jackpot. Moreover, states and various gambling establishments produce glitzy ads that appeal to people’s greed in order to entice them to risk even more than they can afford.
Government should be promoting positive social values such as thrift and integrity rather than negative ones such as greed and avarice. They should be promoting the public welfare rather than seducing citizens to engage in state-sponsored vice.
Economic Costs
Legalized forms of gambling (state lotteries, pari-mutuel betting, and casinos) are often promoted as good economic policy. Proponents say they are painless ways of increasing billions of dollars in state revenue. But there is another economic side to legalized gambling.
First, the gross income statistics for legalized gambling are much higher than the net income. State lotteries are one example. Although about half the states have lotteries and the figures vary from state to state, we can work with some average figures. Generally, the cost of management, advertising, and promotion is approximately sixty cents of each dollar. In other words, for every dollar raised in a lottery, only forty cents goes to the state budget. By contrast, direct taxation of the citizens costs only about one cent on the dollar, so that for every dollar raised by taxes, ninety-nine cents goes to the state.
Second, gambling adversely affects a state economy. Legalized gambling depresses businesses because it diverts money that could have been spent in the capital economy into gambling that does not stimulate the economy. Boarded-up businesses surrounding casinos are a visible reminder of this, but the effect on the entire economy is even more devastating than may be at first apparent. Money that could be invested, loaned, and recycled through the economy is instead risked in a legalized gambling scheme.
Legalized gambling siphons off a lot of money from the economy. More money is wagered on gambling than is spent on elementary and secondary education ($286 billion versus $213 billion in 1990).{21} Historian John Ezel concludes in his book, Fortune’s Merry Wheel, “If history teaches us anything, a study of over 1,300 legal lotteries held in the United States proves . . . they cost more than they brought in if their total impact on society is reckoned.”{22}
Biblical Perspective
Even though the Bible does not directly address gambling, a number of principles can be derived from Scripture. First, the Bible emphasizes a number of truths that conflict with gambling. The Bible, for example, emphasizes the sovereignty of God (Matt. 10:29–30). Gambling, however, is based on chance. The Bible admonishes people to work creatively and for the benefit of others (Eph. 4:28), while gambling fosters a something-for-nothing attitude. The Bible condemns materialism (Matt. 6:24–25) while gambling promotes it.
Gambling breeds a form of covetousness, whereas the tenth commandment (Exod. 20:17) admonishes people not to covet. Coveting, greed, and selfishness are the base emotions that entice individuals to gamble. Christians should be concerned about gambling if for no other reason than the effect it has on the “weaker brother” and how it will affect the compulsive gambler. State-sponsored gambling makes it more difficult for compulsive gamblers to reform. Legalized gambling becomes an institutionalized form of greed.
Second, gambling destroys the work ethic. Two key biblical passages deal with the work ethic. In Colossians 3:23–24 the apostle Paul wrote, “Whatever you do, work at it with all your heart, as working for the Lord, not for men, since you know that you will receive an inheritance from the Lord as a reward. It is the Lord Christ you are serving.” And in 2 Thessalonians 3:7,10, he stated, “For you yourselves know how you ought to follow our example. . . . For even when we were with you, we gave you this rule: If a man will not work, he shall not eat.”
The Twentieth Century Fund research group commented, “Gambling’s get-rich-quick appeal appears to mock capitalism’s core values: disciplined work habits, thrift, prudence, adherence to routine, and the relationship between effort and reward.”{23} These core values of the work ethic are all part of the free enterprise system and are part of the Christian life. Gambling corrupts these values, and replaces them with greed and selfishness. Rather than depending on hard work, gamblers depend on luck and chance.
Third, gambling destroys families. Gambling is a major cause of family neglect. Many of the social costs associated with gambling come from a get-rich-quick mindset. As people get caught up in a gambling frenzy, they begin to neglect their families. Money spent on lottery tickets or at racetracks is frequently not risk capital but is income that should be spent on family needs. According to 1 Timothy 5:8, a person who refuses to care for his family is worse than an unbeliever. Parents must provide for their children (2 Cor. 12:14) and eat the bread of their labors (2 Thess. 3:12). When gambling is legalized, it causes people to neglect their God-mandated responsibility to care for their families, and many of those families then often end up on welfare.
Fourth, gambling is a form of state-sponsored greed. Romans 13:4 teaches that government is to be a servant of God, providing order in society and promoting public virtue. Legalized gambling undercuts government’s role and subverts the moral fabric of society through greed and selfishness promoted by a state-sponsored vice.
Since gambling undermines the moral foundations of society and invites corruption in government, Christians must stand against attempts to legalize gambling.
Notes
1. Report of the National Gambling Impact Study Commission, 18 July 1999, 1.
2. “Gambling in America,” Gambling Awareness Action Guide (Nashville: Christian Life Commission, 1984), 5.
3. Sylvia Porter, “Economic Costs of Compulsive Gambling in U.S. Staggering,” Dallas Morning News, 4 January 1984, 6C.
4. The Final Report of the Commission on the Review of the National Policy toward Gambling, 1976, 65.
5. Charles Colson, “The Myth of the Money Tree,” Christianity Today, 10 July 1987, 64.
6. Gary Becker, “Higher Sin Taxes: A Low Blow to the Poor,” Business Week, 5 June 1989, 23.
7. J. Emmett Henderson, State Lottery: The Absolute Worst Form of Legalized Gambling (Atlanta, GA: Georgia Council on Moral and Civil Concerns, n.d.). 11.
8. Brad Edmonson, “Demographics of Gambling,” American Demographics, July 1986, 40-41.
9. Curt Suplee, “Lotto Baloney,” Harper’s, July 1983, 19.
10. T. Dielman, “Gambling: A Social Problem?” Journal of Social Issues 35, No. 3 (1979), 39.
11. Julian Taber, “Opinion,” USA Today, 14 August 1989, 4.
12. Borden Cole and Sidney Margolis, When You Gamble-You Risk More Than Your Money (New York: Public Affairs Pamplet, 1964), 12.
13. Joseph Shapiro, “America’s Gambling Fever,” U.S. News and World Report, 15 January 1996, 58.
14. John Warren Kindt, statement before a hearing of the U.S. House of Representatives Committe on Small Business, 21 September 1994.
15. “State Lotteries and Gambling-Results Have Not Equaled Expectations,” USA Today, April 1979 (Vol. 107, No. 2407), 1.
16. New York Times, 9 February 1980.
17. Charles Clotfelter and Philip Cook, Selling Hope: State Lotteries in America (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1991).
18. Emmett Henderson, State Lottery: The Absolute Worst Form of Legalized Gambling (Atlanta: Georgia Council on Moral and Civil Concerns, n.d.), 26.
19. Final Report of the Commission on the Review of National Policy toward Gambling, 1976, 71.
20. John Warren Kindt, “The Economic Aspects of Legalized Gambling Activities,” Duke Law Review, 43 (1994): 59.
21. David Neff and Thomas Giles, “Feeding the Monster Called More,” Christianity Today, 25 November 1991, 20.
22. Quoted by William Petersen, What You Should Know about Gambling (New Canaan, CT: Keats, 1973), 37.
23. James Mann, “Gambling Rage: Out of Control,” U.S. News and World Report, 30 May 1983, 30.
© 2005 Probe Ministries
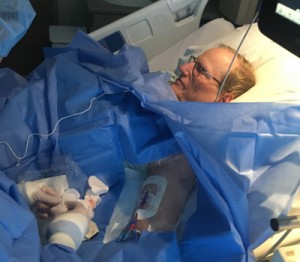 His lower back, where he’d had back surgery six weeks before, was wet. His t-shirt was wet. The sheet was wet. His fingers glistening with a strange wetness from reaching back to investigate, he asked me to check what was going on. I saw a rivulet of fluid pouring out of the top of his surgical incision. Something was really, really wrong.
His lower back, where he’d had back surgery six weeks before, was wet. His t-shirt was wet. The sheet was wet. His fingers glistening with a strange wetness from reaching back to investigate, he asked me to check what was going on. I saw a rivulet of fluid pouring out of the top of his surgical incision. Something was really, really wrong.
 Disneyland has long positioned itself as “The Happiest Place on Earth.” And Disney goes to great lengths to maintain that illusion. Their parks are as close to spotless as you can get; you never see wrappers, gum or spilled popcorn on the ground, since they get swept up within a minute of hitting the pavement by an army of “cast members,” from custodians to ride workers, who are devoted to maintaining the fantasy. Every Disney park cast member is trained to be assertively friendly in making things right and keeping people happy. When a friend’s child lost the ice cream scoop from his cone, within moments a Disney person replaced it for free.
Disneyland has long positioned itself as “The Happiest Place on Earth.” And Disney goes to great lengths to maintain that illusion. Their parks are as close to spotless as you can get; you never see wrappers, gum or spilled popcorn on the ground, since they get swept up within a minute of hitting the pavement by an army of “cast members,” from custodians to ride workers, who are devoted to maintaining the fantasy. Every Disney park cast member is trained to be assertively friendly in making things right and keeping people happy. When a friend’s child lost the ice cream scoop from his cone, within moments a Disney person replaced it for free.