Steve Cable discusses Probe’s survey findings on these topics. He reveals that most Born Again Protestants are not looking to the Bible for help in moral choices and do not think they should let their Christian faith impact their political positions.
Continuing our series examining the results from Probe’s 2020 survey on American religious beliefs and behaviors, we will consider three topics that are important to any society:
1. What most influences your moral choices? Our survey shows that among adults under 40, less than half of those claiming to be Born Again Protestants{1} look to biblical teachings as their primary resource for moral choices. Even among the minority group who look to the Bible, less than half of them would apply a biblical view of monogamous behavior to their choices regarding sex outside of marriage.
2. Do you mix your religious views with your political views? Almost two thirds of Born Again Protestants under 40 agree that one should not let your religious faith impact your political positions. As a Christian, we are to take every thought captive in obedience to Christ{2} who is the source of real truth. Every position we take in every area of life should be informed by our faith in Christ.
3. Where do you learn how to bring about justice across our society? While our government and educational leaders are pushing schools to take action and teach principles of justice without even telling the parents, over two thirds of younger adult Americans across all religious backgrounds believe that parents should be the primary source in teaching ways to stand for justice in our society.
If you have a society where 1) moral questions are answered by popular opinion rather than the Bible, 2) religious faith has no place in informing one’s political stances, and 3) social justice training is left to the state, you are in danger of becoming a totalitarian state where all thinking is controlled for the benefit of the government or some other power bloc within your society. In an alternative society where 1) moral guidance is provided by consulting biblical teaching, 2) one can bring their religion’s teaching into the domain of political discourse, and 3) your thinking on social justice is informed by your religious beliefs, you are in danger of having a democracy where everyone is allowed to develop and express their opinion.
Let’s examine our survey results in more detail to see where American adults stand on these topics.
Making Moral Choices
Our first question deals with where people go for guidance in making moral choices, as laid out below:
When you are faced with a personal moral choice, which one of the following statements best describes how you will most likely decide what to do?
- Do what makes the most people happy.
- Do what your family or friends would expect you to do.
- Do what you believe most people would do under similar circumstances.
- Do what biblical principles teach.
- Do what seems right to me at the time.
- Do what will produce the best outcome for yourself.
- Other
For our analysis, we combined answers 1, 2 and 3 as answers where people are looking to see what other people think. Across all Americans ages 18 through 55, almost four in twenty (20%) people selected one of those three answers{3}. However, those 40 and over were less likely to select one of those three answers, at only about three in twenty (15%). Those under age 40 saw closer to five in twenty (23%) select one of those three.
Let’s look more closely at respondents from ages 18 through 39. Key parts of the results are summarized in the table below.
|
Source |
Born |
Other |
Catholic |
Unaffiliated |
|
What other |
15% |
24% |
29% |
20% |
|
What seems right |
27% |
40% |
40% |
58% |
|
Sum of first two |
42% |
64% |
69% |
78% |
|
Biblical |
47% |
22% |
12% |
3% |
First consider Born Again Protestants; we see that almost half (47%) look to biblical principles for guidance. That result is somewhat encouraging although possibly misleading, as we will explore below. The encouragement is tempered by the fact over half of them are not primarily looking at biblical principles for moral guidance. This includes over four out of ten (42%) who look to others or to what seems best to them.
The Unaffiliated{4} group are clearly not aligned with evangelical Christian values, with less than three out of 100 (2.7%) looking to biblical principles for guidance. Almost eight in ten (78%) look to others or to what seems best to them.
It is not surprising to most that the Unaffiliated would answer this question differently than Born Again Protestants. What about other Christians who might look to the Bible for moral guidance. As Evangelicals, we often think these other Christians are presenting Jesus as an example for moral living rather than as the one and only source for redemption through His sacrifice. But, for Other Protestants and Catholics, we find two thirds (64%/69%) of them saying they look to others or to what seems best to them for their moral compass. In contrast, Other Protestants show just over one in five (22%) looking to biblical principles, while Catholics are around one in ten (12%
Do Born Again Protestants Really Do What They Say?
Almost half of Born Again Protestants say they use biblical principles to make moral choices. With this survey, we can see if their actions match their stated approach to moral decisions. Specifically, let’s look at those who claim to use biblical principles and see if they applied those to their ideas about sexuality. Let’s use two questions on which the Bible provides clear moral guidance.
1. Sex among unmarried people is always a mistake: from Agree Strongly to Disagree Strongly
2. Living with someone in a sexual relationship before marriage:
a. Might be helpful but should be entered into with caution.
b. Makes sense in today’s cultural environment.
c. Will have a negative effect on the relationship.
d. Should be avoided as not our best choice as instructed by God
The Bible clearly states that fornication (sex between people who are not married to each other) is always a mistake. Thus, they should select Agree Strongly for the first question. Living with someone in a sexual relationship is also fornication. They should select answer d. for that question. For our discussion, we will call someone who answered these two questions as shown a Supporter of Sexual Purity.
Now let’s look at how these two questions on sexual morality relate to the answer on moral choices in the table below.
|
Specific |
Born |
Other |
|
1. Use Biblical Principles |
47% |
22% |
|
2. Supporter of |
25% |
3.7% |
|
3. Use Biblical |
21% |
3.1% |
|
4. % of those who |
45% |
14% |
|
5. % of those who |
85% |
82% |
I realize that your eyes may have glazed over when looking over this table. So, let me explain the primary result. In Row 4, we see 45% under the Born Again Protestant column. This means that less than half of the Born Again Protestants who said they used Biblical Principles in making moral choices ALSO selected the biblical position on the two questions relating to fornication. For the other Protestants it was much worse, with only one in seven (14%) selecting to Support Sexual Purity.
What do we make of this disconnect? Either those whose supported Biblical Principles picked areas where they chose not to apply Biblical Principles OR those who supported Biblical Principles do not understand what the Bible says about sexual purity. Both of those choices are a disconcerting view of the fractured worldviews held by many Born Again Protestants.
We also note in row 5, that almost all of those who select to Support Sexual Purity also said they would use Biblical Principles in making moral choices. This figure seems to show that those who do not use Biblical Principles are much more consistent in rejecting biblical morality.
Religion and Politics
The second question deals with how we relate our religious thinking and our political thinking. The question asked was:
Just as the government should not be involved in the internal workings of churches, Christians should not let their faith impact their position on how government functions. Responses from Agree Strongly to Disagree Strongly.
A person’s understanding of religious principles should drive their thinking on any political questions which intersect with a religious principle. We should expect not only Christians but people of every religion to disagree strongly with this statement. For a genuine Christian, their faith in Jesus Christ and the teaching of the Bible are the foundation for all of their beliefs. As Jesus said, “I am the way, the truth and the life (John 14:6).” If we want to apply truth to our position on how government functions, we must look to the source of real truth, Jesus.
Christians can genuinely disagree about the best way to achieve certain objectives. For example, we know Jesus calls us to show concern for the poor and for widows and orphans. However, we may disagree on the best way to carry this out within the structure of our society. But any political approach we choose to support should not contradict our underlying faith position related to the issue at hand.
We can see how people responded to this question in the table below.
|
Faith should not |
Age |
Born |
Other |
Catholic |
Unaffiliated |
|
Strongly |
18 |
21% |
6% |
8% |
5% |
|
Disagree or |
39% |
19% |
23% |
14% |
|
|
Disagree or |
40 |
58% |
23% |
26% |
20% |
Looking at Born Again Protestants, this group is much more likely than other groups to strongly Disagree or Disagree with the statement.
Among those ages 18 to 39, we see that about one in five (21%) Strongly Disagree and close to four out of ten (39%) Disagree or Strongly Disagree. A significant number appear to realize that you cannot segregate your faith beliefs from your beliefs about how our government should operate. However, for this age group, the vast majority, almost two out of three (61%), either agree with the statement or don’t know. This majority buys into the lie that their religious faith should not impact their political beliefs.
Secondly, we see a significant difference in the answers based on the age of the Born Again Protestants. For those ages 40 through 55, we find almost six out of ten (58%) disagree or strongly disagree. Younger adults have been brought up in a society that constantly warns them to leave their religious beliefs at home. Do not bring them to the public square as they are not welcome or appropriate. Those over the age of 40 are much more likely to reject this popular mantra and bring their religious beliefs into the political arena.
Of those Born Again Protestants under the age of 40 who say that their faith has a significant impact on their daily lives, over two thirds (70%) of them also say they make moral choices relying on biblical principles. This is a consistent result, for if faith has a significant impact on your daily life, one would expect it to impact your moral choices. But at the same time, less than one third (29%) of these Born Again Protestants with faith important in their daily lives said they strongly disagreed with the statement that our faith should not impact our political positions. Clearly some combination of the news media, secular education and politicians have succeeded in misguiding Americans on this topic. Many have bought into the false model that political positions are not moral decisions.
Finally, let’s note that significantly less than one out of ten people who are not Born Again Protestants strongly disagreed with the statement. Other Protestants and Catholics are not distinctly different than the Unaffiliated this muddled thinking.
Bringing About Social Justice
Most Americans probably want a fair and just society where law abiding citizens have fair access to opportunity and can apply themselves
toward achieving their life goals. However, there are many different ideas on how to best achieve such an objective. So, we asked this question:
Matters of social injustice like racial prejudice and bullying are best remedied by (rank from 1, most important to 5, least important):
- Government laws and penalties
- Churches teaching on how to live with and treat others
- Parents overtly teaching their children how to treat others
- Parents showing their children by example
- School curricula focused on correct social thinking
As noted in the question, respondents were asked to rank the five responses rather than pick the best one. We did this because we felt that many people would have more than one approach they considered important.
Let’s begin by considering the options that were ranked as most important. In our evaluation, we combined the two options featuring parents as one item.
|
First Choice |
Born Again Protestant |
Other Protestant |
Catholic |
Unaffiliated |
|
Parental |
69% |
53% |
66% |
73% |
|
Church |
21% |
19% |
19% |
8% |
|
Government |
9% |
15% |
9% |
11% |
|
School |
1% |
14% |
6% |
8% |
As shown, parental guidance was by far the most popular choice across all religious backgrounds averaging about two thirds of the responses. Except for the Unaffiliated, church teaching was a distant second, polling about one out of five for the other religious groupings.
Let’s consider the other extreme, the response selected as their least favorite choice by our respondents. Except for the Unaffiliated, the least popular option was school curricula focusing on correct social thinking. This option was selected last by about four out of ten respondents across all of the religious groups. Naturally, more than half of the Unaffiliated selected Church Teaching as their least favorite choice. For Born Again Protestants, government laws were selected as least favorite at almost the same level as school curricula.
As you can see, most Americans would say that remedying social injustice required parental involvement while school curricula was the least popular option. Thus, it is very interesting that many politicians and educators want to make the school the primary place for remedying social injustice while protecting the students from the poor examples of their parents. This may well be why that at the time this is being written that some school boards are seeing a significant change in their make up as pro-parental rights candidates are being elected.
Notes
1. Born Again Protestants affiliate with a Protestant denomination, have had an experience with Jesus Christ that is still important in their lives today, and state they will go to heaven because they confessed their sins and accepted Jesus Christ as their savior.
2. 2 Corinthians 10:5
3. Each of the three answers accounted for about 7% of the respondents.
4. The Unaffiliated include atheists, agnostics and those who believe nothing in particular.
© Probe Ministries 2022
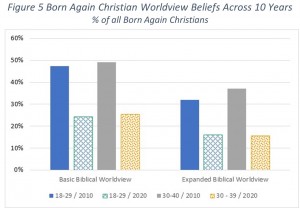 Now let’s compare these 2020 results with the results from our 2010 survey. Figure 5 shows the results across this decade for Born Again Christians looking at the percent who agree with the worldview answers above. As shown, there has been a dramatic drop in both the Basic Biblical Worldview and the Expanded Biblical Worldview.
Now let’s compare these 2020 results with the results from our 2010 survey. Figure 5 shows the results across this decade for Born Again Christians looking at the percent who agree with the worldview answers above. As shown, there has been a dramatic drop in both the Basic Biblical Worldview and the Expanded Biblical Worldview.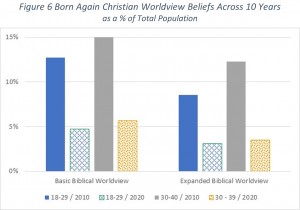 However, because the percent of the population who profess to being born again has dropped over the last ten years as well, the situation is even worse. We need to look at the percent of Americans of a particular age range who hold to a Biblical Worldview. Those results are shown in Figure 6. Once again, comparing the 18–29 age group from 2010 with the same age group ten years later now 30–39, we find an even greater drop off. For the Basic Biblical Worldview, we see a drop off from 13% of the population down to 6%. For the Expanded Biblical Worldview, the decline is from 9% down to just over 3% (a drop off of two thirds).
However, because the percent of the population who profess to being born again has dropped over the last ten years as well, the situation is even worse. We need to look at the percent of Americans of a particular age range who hold to a Biblical Worldview. Those results are shown in Figure 6. Once again, comparing the 18–29 age group from 2010 with the same age group ten years later now 30–39, we find an even greater drop off. For the Basic Biblical Worldview, we see a drop off from 13% of the population down to 6%. For the Expanded Biblical Worldview, the decline is from 9% down to just over 3% (a drop off of two thirds).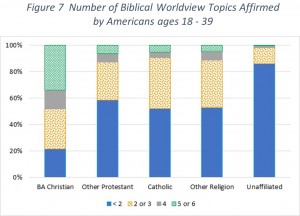 Rather than look at the two biblical worldview levels discussed above, we will look at how many of the six biblical worldview questions they answered were consistent with a biblical worldview. In the chart, we look at 18- to 39-year-old individuals grouped by religious affiliation and map what portion answered less than two of the questions biblically, two or three, four, or more than four (i.e., five or six).
Rather than look at the two biblical worldview levels discussed above, we will look at how many of the six biblical worldview questions they answered were consistent with a biblical worldview. In the chart, we look at 18- to 39-year-old individuals grouped by religious affiliation and map what portion answered less than two of the questions biblically, two or three, four, or more than four (i.e., five or six).