Dr. Patrick Zukeran critiques Rob Bell’s controversial book denying the biblical teaching on hell, arguing that Bell offers another gospel.
A New Kind of “Christianity”
 Will all people regardless of their belief enter heaven? In a new book, Love Wins, mega church pastor Rob Bell presents his case for universal salvation. Bell states that a Christianity that teaches many will spend eternity in hell while some go to heaven is “misguided and toxic.”{1} Bell asserts that the message Christians have preached for centuries is actually a harmful message.
Will all people regardless of their belief enter heaven? In a new book, Love Wins, mega church pastor Rob Bell presents his case for universal salvation. Bell states that a Christianity that teaches many will spend eternity in hell while some go to heaven is “misguided and toxic.”{1} Bell asserts that the message Christians have preached for centuries is actually a harmful message.
Bell argues that God loves everyone and desires all people to be saved. However if the majority of people never come to faith in Christ and spend eternity in hell, God fails to accomplish His will. Since this is not an acceptable conclusion, the only logical conclusion left is that in the end, all will eventually receive His love and enter into heaven.
Bell begins by bombarding the reader with hundreds of questions. The questions are meant to challenge and expose the alleged inconsistencies of traditional teachings and prepare you for his case for universal salvation. On page 1 he writes,
Will only a few select people make it to heaven, and will billions and billions of people burn forever in hell? And if that’s the case, how do you know? How do you become one of the few? Is it what you believe, or what you say, or what you do, or who you know, or something that happens in your heart, or do you need to be initiated, or baptized, or take a class, or converted, or be born again? How does someone become one of these few? And then there’s a question behind the question—the real question: What is God like? Because millions and millions of people who were taught that the primary message, this center of the Gospel of Jesus, is that God is going to send you to hell unless you believe in Jesus. And so what got subtly sort of caught and taught is that Jesus rescues you from God. But what kind of God is that that we would need to be rescued from this God? How could that God ever be good? How could that God ever be trusted? And how could that ever be good news?{2}
 These are good questions and deserve to be asked. “Traditional” beliefs may not always be right, and at times they deserve to be reexamined. Bell then in the final pages of his preface implies that those who oppose his view are judgmental and not open to discussion of vital doctrines of the faith. This is part of his strategy to discourage any criticism of his position. However, Scripture calls us to evaluate all teachings and discern truth from error (1 Thess. 5:21; 1 Jn. 4:1).
These are good questions and deserve to be asked. “Traditional” beliefs may not always be right, and at times they deserve to be reexamined. Bell then in the final pages of his preface implies that those who oppose his view are judgmental and not open to discussion of vital doctrines of the faith. This is part of his strategy to discourage any criticism of his position. However, Scripture calls us to evaluate all teachings and discern truth from error (1 Thess. 5:21; 1 Jn. 4:1).
In the process of defending his thesis, Bell ends up presenting a new kind of Gospel. Since theological doctrines are connected, when you change the gospel message there is a chain effect that follows. His gospel ends up presenting a distorted understanding of God’s character, a variant view of the atonement, and a heaven and hell foreign to the scriptures.
Bell struggles with a significant question: “Will those without Christ truly spend eternity in hell? Could there be a possibility that they have a chance after death to repent?” The idea that a loved one will spend eternity in hell is a difficult one to accept. Careful study of all the relevant scriptures is necessary when we examine a particular doctrine, especially one regarding our salvation. If in the end we are faced with a conclusion we do not like, we must not compromise biblical truth but accept the words of Christ. Paul warns us in Galatians 1:9 the danger of preaching another gospel. When it comes to essential doctrines of the faith, Christians cannot compromise on the truths taught in Scripture. For this reason we must carefully examine Bell’s teachings and see if it is compatible with, or a compromise of, the gospel of Christ.
Another Kind of Gospel
To support his thesis that all individuals will eventually enter into heaven, Bell must alter the gospel message. He admits that his message departs from traditional Christianity and declares that the message preached for past centuries is misguided and in need of transformation.
A staggering number of people have been taught that a select few Christians will spend forever in a peaceful, joyous place called heaven while the rest of humanity spends forever in torment and punishment in hell with no chance for anything better. It’s been clearly communicated to many that this belief is a central truth of the Christian faith and to reject it is, in essence, to reject Jesus. This is misguided, toxic, and ultimately subverts the contagious spread of Jesus’ message of love, peace, forgiveness and joy that our world desperately needs to hear.{3}
The traditional message that salvation comes only to those who accept Christ in their lifetime is rejected by Bell. He believes that all people are reconciled to God through Christ’s death on the cross regardless of whether they choose to put their faith in Christ or not. Those who do not receive Christ in this lifetime will spend some time in hell but no one will remain there forever. Eventually all people will respond to God’s love, even those in hell and enter heaven. Bell states this on several occasions:
At the heart of this perspective is the belief that, given enough time, everybody will turn to God and find themselves in the joy and peace of God’s presence. The love of God will melt every hard heart, and even the most “depraved sinners” will eventually give up their resistance and turn to God.{4}
To be clear, again, an untold number of serious disciples of Jesus across hundreds of years have assumed, affirmed, and trusted that no one can resist God’s pursuit forever, because God’s love will eventually melt even the hardest of hearts.{5}
At the center of the Christian tradition since the first church have been a number who insist that history is not tragic, hell is not forever, and love, in the end, wins and all will be reconciled to God.{6}
Within this proper, larger understanding of just what the Jesus story even is, we see that Jesus himself, again and again, demonstrates how seriously he takes his role in saving and rescuing and redeeming not just everything but everybody.{7}
Bell points to several Scriptures to support his argument. One passage is 1 Corinthians 13 which states, “Love never fails.” Therefore he concludes, God’s love will reach all lost people even those in hell and they will eventually turn to Him since no one can resist God’s love forever.
However, there are many passages in the Bible that teach the unrighteous are eternally separated from God and the righteous are forever with God. Daniel 12:2 speaks of a future resurrection and eternal destiny for the righteous and unrighteous: “Multitudes who sleep in the dust of the earth will awake: some to everlasting life, others to shame and everlasting contempt.” Daniel states that there will be a resurrection and judgment of all people. Some will inherit eternal life and others will suffer “everlasting contempt.” Daniel teaches in this passage that not all individuals will enter into everlasting life. Those who do not are destined to “everlasting contempt.” The Hebrew word for everlasting is ôlām. The word in this context signifies an indefinite futurity, forever, or always. It refers to an unending future.{8} This is the most likely definition for ôlām used later in verse 7 referring to the eternal nature of God: “And I heard the man clothed in linen, who was above the waters of the stream; he raised his right hand and his left hand toward heaven and swore by him who lives forever…” We know that God is eternal. Therefore, Daniel is using the term “ôlām” to mean everlasting and never ending.
Jude 7 states, “In a similar way, Sodom and Gomorrah and the surrounding towns gave themselves up to sexual immorality and perversion. They serve as an example of those who suffer the punishment of eternal fire.” The Greek word for eternal is aiṓnios which means “eternal, perpetual, to time in its duration, constant, abiding. When referring to eternal life, it means the life which is God’s and hence it is not affected by the limitations of time.”{9} The word again is used in verse 21 to refer to “eternal” or never ending life with God. So in the context of Jude aiṓnios is used to refer to an eternal state.
In Matthew 7:13-14 Jesus invites, “Enter through the narrow gate, for the gate is wide and the way is broad that leads to destruction, and there are many who enter through it. For the gate is small and the way is narrow that leads to life, and there are few who find it.” Jesus taught an exclusive view of salvation. He stated clearly not everyone will inherit eternal life; in fact many will follow the path of destruction. This verse speaks against the doctrine of universal salvation.
Hebrews 9:27 (“it is appointed for men to die once and after this comes judgment”) teaches that there is no second chance for salvation after death. The preceding verses teach that Christ made the perfect sacrifice for sin once and for all. He paid the price once and His sacrifice is for all time. In the same way that Christ’s atonement is final, so all men and women die once and face a judgment which is final and eternal in its sentence.
Bell’s gospel is a departure from biblical teaching. God is love and therefore, He does not impose His will on those who refuse to receive His love. He honors the choice of individuals to receive or reject Him. Those who reject Him in this life will not want to be with Him for all eternity. God honors their choice and places them away from His presence in hell. Thus, God’s character of love honoring one’s choice is upheld. But God’s character of justice in dealing with sin is also upheld.
Are All Reconciled to God?
There are several key passages Bell uses to support his thesis that all individuals will eventually enter heaven. One key verse that deserves attention is Colossians 1:20, a favorite verse used by many universalists: “and through him (Jesus) to reconcile to himself all things, whether things on earth or things in heaven, by making peace through his blood, shed on the cross.” According to Bell, the entire world is reconciled to God through the death of Christ. Christ’s death has atoned for all sin and places every person in right standing with God. Those who turn to God in this life will enter heaven immediately. Those who reject God’s love in this lifetime will be temporarily separated from God in hell but will eventually receive His love and enter heaven.
Contrary to Bell’s interpretation, this verse does not teach a universal salvation. Rather, it presents the scope, goal, and means of reconciliation. The scope of reconciliation extends not just to human beings but to all of creation which was affected by sin. Romans 8:20-22 says,
For the creation was subjected to futility, not willingly, but because of him who subjected it, in hope that the creation itself will be set free from its bondage to corruption and obtain the freedom of the glory of the children of God. For we know that the whole creation has been groaning together in the pains of childbirth until now.
The physical world was affected by sin, not by its choice but by the choice of Adam. Christ’s victory over sin restored order over creation by bringing it again under His lordship, and full restoration will take place in the future.{10}
Angels and human beings, unlike the material world, have a choice. Reconciliation involves two parties who voluntarily decide to make peace. In this case fallen angels knowingly rebelled against Christ and reconciliation is not possible. Humans also must make a choice to receive God’s invitation through Christ or to reject it. This is made clear in the following verses:
And you, who once were alienated and hostile in mind, doing evil deeds, he has now reconciled in his body of flesh by his death, in order to present you holy and blameless and above reproach before him, if indeed you continue in the faith, stable and steadfast, not shifting from the hope of the gospel that you heard, which has been proclaimed in all creation under heaven, and of which I, Paul, became a minister. (Col. 1:21-23)
Paul states that we were once “alienated” from God and we are reconciled “if indeed you continue in the faith . . . not shifting from the hope of the gospel.” The reconciliation depends on the believer receiving Christ by faith and persevering in that faith. Numerous other verses make faith in Christ necessary for reconciliation (Jn. 3:18, 5:24; Rom. 1:17; 3:21-26).
Those who receive God’s gift of life will attain blessings and salvation. Those who refuse are sentenced to eternal death (Jn. 3:18). In the end all things will be put in their proper place. It is in this context all things will be reconciled to Christ and in submission to His lordship (Phil. 2:5-11).
Another Kind of God
In his effort to defend his thesis that in the end everyone goes to heaven, Rob Bell must alter the message of the gospel. However, in doing so, he also alters the character of God. Among the hundreds of questions with which Bell bombards his readers, he asks the following: “If there are only a select few who go to heaven, which is more terrifying to fathom: the billions who burn forever or the few who escape this fate? How does a person end up being one of the few? Chance? Luck? Random selection? . . . God choosing you instead of others? What kind of faith is that? Or, more important: what kind of God is that?”{11} For Bell, a God who would send billions to an eternal hell would not be a God of love. However, in emphasizing God’s character of love he ends up ignoring God’s other attributes, and in the end alters the character of God.
Bell is correct in stating that God is love. However, he commits an error common among universalists. Bell ends up presenting an imbalanced view of God that emphasizes God’s character of love to the neglect of the other character qualities of God. Love is not the only or the most dominant character of God. Along with love, God has other character qualities which exist together in a perfect balance.
Among the numerous qualities of God, the Bible teaches that God is also just (2 Thess. 1:6), He is holy (Isa 6:3), He is righteous (Ps. 7:11), sovereign (Jude 4), wise (1 Cor. 3:19) true (Jn. 14:6), etc. There are many qualities of God that are just as important as love, and they exist in a perfect balance. Thus, emphasizing one trait to the exclusion of others leads to flawed theology.
God is love and God desires that all individuals be saved. However, God is also just and holy and must deal righteously with sin. God’s character of holiness is well emphasized throughout the Bible. This is the theme of Leviticus and, throughout this book, God presents detailed instructions for dealing with sin through the sacrificial system. The Levitical sacrifices are fulfilled in the death of Christ who fulfills the righteousness of God.
The theme in the prophets is that Israel has violated the holiness of God and thus God must judge their sins. Isaiah 5:16 states, “But the Lord Almighty will be exalted by his justice, and the holy God will show himself holy by his righteousness.” God, being a loving God, sent prophets to warn Israel to turn from their idolatry and disobedience and return to Him. However, after generations of refusal by Israel, God finally had to judge the sins of the people. Throughout the New Testament, Christians are exhorted to live holy lives for that reflects the character of God (Eph. 4:24; Heb. 12:14; 1 Pet. 1:15-6).
Those who refuse the gift of Christ’s work on the cross have not been cleansed from their sin and therefore cannot enter the holy presence of God. This is the theme of Hebrews 9, which teaches us that access to God represented in the Holy of Holies at the Temple was not accessible to us. However, the blood of Christ fulfilled the holiness of God and cleansed sinners and made us holy before God. Only through the blood of Christ is this made possible.
Bell emphasizes God’s love but diminishes His holiness and righteousness; therefore, the magnitude of our sin, its effect on our nature, and it offense to God are diminished. God hates sin and judges sin seriously. In Revelation, the wrath of God is poured out upon the world in rebellion. In Revelation 20, those individuals not found in the book of life are thrown into the lake of fire. To build a picture of God who is excluded of His holiness, justice and righteousness, who does not judge sin, is to present an imbalanced and false view of God.
Bell argues,
Millions have been taught that if they don’t believe, if they don’t accept in the right way, . . . God would have no choice but to punish them forever in conscious torment in hell. God would in essence become a fundamentally different being to them in that moment of death, a different being to them forever. A loving heavenly father who will go to extraordinary lengths to have a relationship with them would, in the blink of an eye, become a cruel, mean, vicious tormenter who would ensure that they had no escape from an endless future of agony. . . . If God can switch gears like that, switch entire modes of being that quickly, that raises a thousand questions about whether a being like that could ever be trusted, let alone good.{12}
Bell argues that God changes according to the decision of individuals. However, God is not the one who changes. He is always loving and reaching out to all people, but He is also holy and righteous and and must deal justly with sin. Those who do not want to be with God now will not want to be with Him in eternity. Because He is love, He does not force people to be with Him for eternity but honors their choice. God allows them to exist away from Him in hell. So God does not change; He grants individuals what they desire.
I would also disagree with Bell’s statement that God is the one tormenting individuals. Torment comes from within the person. The torment the person experiences is not inflicted by God but comes from the individual who must live eternally with his or her decision to reject the love of God. Therefore hell honors the free choice of men and fulfills the love of God who does not impose Himself on those who do not want Him. It also fulfills His holiness, removing sin from His presence.
Another Kind of Heaven and Hell
To maintain his thesis that everyone will go to heaven, Rob Bell must alter the gospel message, the character of God, and the teaching on heaven and hell. Bell teaches that hell is not eternal but temporary, and in fact heaven and hell are actually the same place. For those who have accepted God’s love, this place will be heaven. For those who continue to reject God’s love this place will be hell. Hell is created by the individual who resists God’s love. Bell states, “We create hell whenever we fail to trust God’s retelling of our story.”{13} The individual remains in this condition until he is won over by God’s love and eventually turns to God. Then what was once hell will becomes heaven.
Bell derives this from Luke 15, the Parable of the Prodigal Son. In this story, after the younger brother returns, the father throws this formerly lost son a big banquet. However, the older brother, jealous and upset over his younger brother’s reception, remains outside and chooses not to enjoy the party. Both brothers are in the same place but for one it is a party, for the other it is miserable.{14} Bell states that it is our choice. “We’re at the party, but we don’t have to join in. Heaven or hell. Both are at the party.”{15} The younger brother who has received his father’s love it is a joyous time, but for the older brother who has the wrong view of his father it is misery.
Bell is really stretching the interpretation of this parable to support his theology. I am not aware of any New Testament scholar that finds this doctrine of heaven and hell in this parable. The parable comes in the context of the Pharisees and teachers of the law questioning Jesus associating with “sinners.” Jesus, in defense of His ministry and displaying the compassion of God for the lost, tells three parables: the lost sheep, the lost coin, and the lost son. The younger brother represents the sinners who repent and turn to God while the older brother represents the Pharisees and teachers of the law who have little compassion for the lost.{16} So the purpose of the parable is God’s heart for the lost and the cold heartedness of the Pharisees and teachers of the law. To read into this story Bell’s doctrine of heaven and hell is a stretch. It does not appear Jesus had in mind any teaching on heaven and hell in this parable.
Bell believes that heaven and hell are actually the same place and he also believes that hell is not permanent. He describes it as a “period of pruning” and “an intense experience of correction.”{17} It appears that Bell views hell similar to the Catholic teaching of purgatory. Eventually this will end when the person turns to God because, according to Bell, “No one can resist God’s pursuit forever because God’s love will eventually melt even the hardest hearts.”{18}
Another way Bell defends his doctrine of hell is in doing a brief word study. The Old Testament word is sheol. Bell explains that sheol is the place of the grave in the Old Testament and that it speaks generally of the resting place of the departed sprits. Three words are used in the New Testament: gehenna, hades, and tartarus. Gehenna, he says, is the Valley of Hinnon, the garbage dump outside Jerusalem.{19} The word tartarus comes from Greek mythology, referring to the underworld where Greek demigods were judged.{20} Hades, he states, is the equivalent of the Hebrew sheol, an obscure, dark and murky place.{21} He thus concludes from his brief word study on hell that hell is not clearly defined in the Bible and that holding to the belief that it is a place of eternal suffering is unjustified.
Bell correctly states that sheol is the place of the grave and speaks generally of the place where the departed spirits go. There are several occasions where Old Testament saints stated they would go to sheol. However, his word study is incomplete. As revelation progresses, we see there are different fates for the righteous and the wicked. There is indeed a judgment which determines the destiny of individuals.
As mentioned above, Daniel 12:2 speaks of a future resurrection and eternal destiny. “Multitudes who sleep in the dust of the earth will awake: some to everlasting life, others to shame and everlasting contempt.” Daniel states that there will be a resurrection and a judgment that determines the eternal destiny of individuals. Some will resurrect to eternal life while others to everlasting contempt. As noted earlier, the Hebrew word for everlasting is ôlām. Olām is used more than three hundred times to indicate indefinite continuance into the very distant future. There are times it is used to designate a long period in the past or a designated long period of time in the future.{22} Context determines the definition. In this context it signifies an indefinite future or forever. This is the most likely definition for several reasons. First, the context found in verses 1 and 2 speaks of the resurrection at the end of the age. This is speaking of the final judgment before the righteous enter into eternity. Second, in verse 3 it is used of the righteous shining forever. Third, it is used later in verse 7 referring to the eternal nature of God. “And I heard the man clothed in linen, who was above the waters of the stream; he raised his right hand and his left hand toward heaven and swore by him who lives forever.” Daniel describes an eternal state of reward and life for the righteous but an eternal state of contempt for the unbelievers.
In Isaiah 66:22-24, Isaiah speaks of the Lord establishing His kingdom and restoring Israel. He concludes saying, “And they will go out and look upon the dead bodies of those who rebelled against me; their worm will not die, nor will their fire be quenched, and they will be loathsome to all mankind.” Here Isaiah refers to state of eternal torment for those who rebel against the Lord.{23} Although sheol is used of the general resting place of departed spirits, as revelation progresses the Old Testament mentions a different eternal destiny of the righteous and unrighteous. The eternal state is further revealed in the New Testament.
In reference to the New Testament words, the most commonly used word is Gehenna. Bell is correct that Gehenna is derived from the Valley of Hinnon outside of Jerusalem, but once again his word study is incomplete. Gehenna is associated with evil, and, in the context of the New Testament, symbolizes more than just a garbage heap. It served as a physical picture of the eternal state of suffering.
In Matthew 18:7-9 Jesus states, “Woe to the world for temptations to sin! For it is necessary that temptations come, but woe to the one by whom the temptation comes! And if your hand or your foot causes you to sin, cut it off and throw it away. It is better for you to enter life crippled or lame than with two hands or two feet to be thrown into the eternal fire. And if your eye causes you to sin, tear it out and throw it away. It is better for you to enter life with one eye than with two eyes to be thrown into the hell of fire.” The Greek word for “eternal” is aiṓnios. This word means “eternal, perpetual to time in its duration, constant, or abiding.” When referring to eternal life, it means the life which is God’s and hence it is not affected by the limitations of time.{24} The fire described in verse 8 is an eternal and never-ending fire. In the very next verse Christ states that it is better to enter heaven blind in one eye than “be thrown into the hell (Gehenna) of fire.” In just the previous verse, the fire of hell was said to be eternal. From the context then we should conclude Gehenna is an eternal state, not a temporary one.
In Mark 9:47-48 Jesus says, “And if your eye causes you to sin, tear it out. It is better for you to enter the kingdom of God with one eye than with two eyes to be thrown into hell, ‘where their worm does not die and the fire is not quenched.’” Jesus states that in Gehenna, the worm lives eternally and the fire is also eternal. Gehenna then is a described as an eternal abode.
Jesus further states that the punishment in hell is eternal and not temporary. In Matthew 25:46, the judgment of the sheep and the goats, Jesus states, “And these (the goats) will go away into eternal punishment, but the righteous into eternal life.” Bell attempts to show in Matthew 25:46—the separation of the sheep and the goats—that when Jesus said “eternal punishment,” he did not mean the punishment was eternal. He writes, “Aion, we know, has several meanings. One is ‘age’ or ‘period of time’; another refers to intensity of experience. The word kolazo (punishment) is a term from horticulture. It refers to the pruning and trimming f the branches of a plant so it can flourish. . . . Depending on how you translate aion and kolazo, then, the phrase can mean ‘a period of pruning’ or ‘a time of trimming’ or an intense experience or correction.”{25}
However, I find Bell’s explanation unsatisfactory since the verse states that the goats will “go away into eternal punishment, but the righteous into eternal life.” Here the eternal life of the believer is seen in contrast with the eternal judgment of the unbeliever. If he is to be consistent, we must interpret that the righteous will not enter into an eternal state of life in the presence of God but a temporary state of life. However, this would not make any sense in this verse. Why should we understand that the word “eternal” for the righteous means everlasting but it is taken to be a temporary state for the unrighteous? Since the righteous enter everlasting life, we should take the preceding phrase that the goats will enter a state of eternal punishment.
Paul writes in 2 Thess. 1:8-9, “He will punish those who do not know God and do not obey the gospel of our Lord Jesus. They will be punished with everlasting destruction and shut out from the presence of the Lord and from the majesty of his power.” The words “everlasting destruction,” when used together, refer to an eternal state of punishment. The Complete Word Study Dictionary: New Testament states that Ólethros aiṓnios (destruction everlasting) refers to destruction which is eternal or everlasting. It is destruction or a state which is imposed by God forever. In a similar way the phrase “eternal judgment” used in Heb. 6:2 means an eternal sentence imposed by God. All of these designations of punishment stand in contrast to eternal life as the inherent punishment for those who reject Christ’s salvation in that they will be separated from the life of God which they rejected. As to the duration of what is designated as aiṓnios when it comes to punishment, it is only proper to assign it the same duration or endlessness as to the life which is given by God.{26}
Revelation 14:9-11 states, “A third angel followed them and said in a loud voice: ‘If anyone worships the beast and his image and receives his mark on the forehead or on the hand, he, too, will drink of the wine of God’s fury, which has been poured full strength into the cup of his wrath. He will be tormented with burning sulfur in the presence of the holy angels and of the Lamb. And the smoke of their torment rises forever and ever.’” In this passage the Greek word aiṓnios is repeated at the end of verse 11. The phrase “forever and ever” is used twelve times in Revelation. Each time it refers to an eternal existence. Eight times it is associated with the nature of God or the never ending rule of God. For example Revelation 4:9-10 says, “And whenever the living creatures give glory and honor and thanks to him who is seated on the throne, who lives forever and ever, the twenty-four elders fall down before him who is seated on the throne and worship him who lives forever and ever.” The most consistent interpretation of 14:9-11 is that the suffering of the unbelievers is of an eternal nature.
Jude 7 states, “In a similar way, Sodom and Gomorrah and the surrounding towns gave themselves up to sexual immorality and perversion. They serve as an example of those who suffer the punishment of eternal fire.” Once again the word here is aiṓnios, signifying an eternal punishment.
It is difficult to interpret passages like these (2 Thess. 1:9; Jude 7; and Rev. 14:9-11) to mean something other than eternal or never-ending punishment. Bell’s interpretations are incorrect and his word studies are incomplete. When you look at several passages in their context, it is very difficult to support Bell’s view.
How Many Stones Cry Out?
Is Jesus the only way to eternal life or are there other ways to salvation besides Christ? Bell makes his case that there are other ways to eternal life. Bell builds his case from Exodus 17 where Moses struck the rock which brought forth water for the Israelites. In 1 Corinthians 10, Paul states that Christ was that rock which Moses struck. Thus, Bell makes the leap that if Christ was in that rock, it is very likely He is in numerous rocks. Bell writes,
According to Paul, Jesus was there. Without anybody using his name. Without anybody saying that it was him. Without anybody acknowledging just what–or more precisely, who–it was. Paul’s interpretation that Christ was present in the Exodus raises the question: Where else has Christ been present? When else? Who Else? How else? Paul finds Jesus there, in that rock, because Paul finds Jesus everywhere.{27}
It appears Bell is stating that one need not know the gospel message of Christ as taught in the New Testament. A person can be saved through other means and messages. Bell further states,
As obvious as it is, then, Jesus is bigger than any one religion. He didn’t come to start a new religion, and he continually disrupted whatever conventions or systems or establishments that existed in his day. He will always transcend whatever cages and labels are created to contain him, especially the one called Christianity. Within this proper larger understanding of just what the Jesus story even is, we see that Jesus himself, again and again, demonstrates how seriously he takes his role in saving and rescuing and redeeming not just everything, but everybody.{28}
Bell emphasizes that he believes that salvation comes through Jesus and Jesus alone saves all people. He refers to Jesus’ words in John 14:6. However, he believes that Jesus may be found in the numerous other religions but identified by different names, symbols, or teachings for Jesus as the creator is present in all creation. Therefore, Christianity does not have the exclusive message of salvation. Other religions contain the presence of Christ through their teachings. How and where they do, Bell does not explain.
Bell states again that specific knowledge of Jesus and the message of the cross is not necessary for salvation. “What he (Jesus) doesn’t say is how, or when, or in what manner the mechanism functions that gets people to God through him. He doesn’t even state that those coming to the Father through him know they are coming exclusively through him. He simply claims that whatever God is doing in the world to know and redeem and love and restore the world is happening through him.”{29} So for Bell, salvation is possible without understanding who Jesus is, his atoning work, and the message of the cross.
Bell misunderstands the text of John 14:6 [“I am the way, and the truth, and the life; no one comes to the Father but through Me”]. Jesus states that He is the only way to eternal life. The “mechanism” is faith in Jesus Christ. Truth is found in general revelation, creation, and the conscience. Therefore, truth about God can be found studying nature (Rom. 1) and through the moral law within each one of us (Rom. 2). For this reason, there are teachings that are true in other religions. For example, many ethical systems in the other religions overlap with biblical teachings. So truth that points to God can be found in general revelation, but saving knowledge of Christ is not found in general revelation. Salvation comes through the special revelation of Jesus Christ. For this reason Paul states, “How, then, can they call on the one they have not believed in? And how can they believe in the one of whom they have not heard? And how can they hear without someone preaching to them? And how can they preach unless they are sent? As it is written, ‘How beautiful are the feet of those who bring good news!’” (Rom. 10:14-5) Paul states it is only the specific message of the gospel of Jesus Christ that saves (Rom. 1:16).
There are several examples in the New Testament that reveal general revelation was not enough for salvation, but special revelation was needed. In Acts 10, Cornelius, a God-fearing Roman soldier, believes in God and lives a noble life. However, that was not enough. For this reason, God sent Peter to present the message of the gospel to Cornelius. After hearing the gospel message, Cornelius and his family receive the gift of salvation. Therefore, the message of the gospel must be heard and received for salvation.
Jesus further taught that the message of salvation is narrow and exclusive. This is not only the nature of the gospel message but the nature of truth itself. If Jesus is the son of God, any religion that rejects this truth must be false in its salvation message. In Matthew 7:13-14, Jesus stated that the way to eternal life is indeed narrow and only a few find it. Peter reinforced that Jesus is the only way in Acts 4:12, and Paul states in 1 Timothy 2:5 that Jesus is the only mediator between God and man. If these statements are true, then salvation comes exclusively through Jesus.
It is also logically unreasonable to assume that salvation is possible through other religions. For example, Islam rejects the deity of Christ, the death of Christ on the cross, the resurrection, and salvation by faith in Christ. Many forms of Buddhism reject the idea of a God. Hinduism teaches that Brahma is an impersonal force and is in a codependent relationship with the universe since Brahma is made up of all things. Since the other religions have significant teachings contradictory to Christianity, it is unreasonable to conclude they contain the salvation message of Christ.
So do the stones cry out? There is truth in general revelation (creation and the conscience) but this truth does not save; it points one to God (Rom. 1:18-32; 2:12-16). Salvation requires the gospel message of Christ as stated by Paul in 1 Cor. 15, that we are sinners, Christ died for our sins and rose triumphing over sin, and we are called to receive Him as our Lord and Savior. Without the gospel message of Christ, one cannot attain salvation.
Conclusion
Paul warns us very strongly in Galatians 1:8 the danger of preaching another gospel. Unfortunately, Bell here presents another gospel and in doing so, presents a false message of hope that has eternal consequences. In Love Wins, Bell argues that in the end everyone will be in heaven because that is God’s will. No one can resist God’s love forever, and if all are not saved, God is not glorified. However, in changing the gospel message Bell changes the character of God and the nature of heaven and hell. God is a God of love, and in His love He honors the decision of individuals to freely choose Him or reject Him. Those who reject Christ, have not had their sins cleansed and cannot enter into the presence of a holy God. In the end, God upholds His love by honoring the choice of all individuals and upholds his righteousness by placing the righteous in His presence and the unrighteous in hell, away from His holy presence. In the end God wins. That is the message of the cross.
Notes
1. Rob Bell, Love Wins (New York, NY: Harper Collins, 2011), viii.
2. Ibid., 1.
3. Ibid., viii.
4. Ibid., 107.
5. Ibid., 107.
6. Ibid., 109.
7. Ibid., 150.
8. Brown, F., Driver, S. R., & Briggs, C. A.). Enhanced Brown-Driver-Briggs Hebrew and English Lexicon (Oak Harbor, WA: Logos Research Systems electronic ed., 2000), 762.
9. Spiros Zodhiates, The Complete Word Study Dictionary: New Testament (electronic ed.), (Chattanooga, TN: AMG Publishers, 2000).
10. Richard Melick, The New American Commentary: Philippians, Colossians, Philemon (Nashville, TN: Broadman & Holman Publishers, 2001), 225.
11. Bell, Love Wins, 2.
12. Ibid., 172-3.
13. Ibid., 172.
14. Ibid., 170-76.
15. Ibid., 175.
16. J. B. Green, The Gospel of Luke. The New International Commentary on the New Testament (Grand Rapids, MI: Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing Co. 1997), 579.
17. Bell, Love Wins, 91-2.
18. Ibid., 108.
19. Ibid., 68.
20. Ibid., 69.
21. Ibid.
22. A. A. Macrae, “1631 ???,” in R. L. Harris, G. L. Archer, Jr. & B. K. Waltke, eds., Theological Wordbook of the Old Testament, (electronic ed.) (Chicago: Moody Press, 1999), 672.
23. John Walvoord, and Roy Zuck, The Bible Knowledge Commentary : An Exposition of the Scriptures (Wheaton, IL: Victor Books, 1983), Is 66:22-24.
24. Zodhiates, The Complete Word Study Dictionary: New Testament.
25. Bell, Love Wins, 90-1.
26. Zodhiates, The Complete Word Study Dictionary: New Testament.
26. Bell, Love Wins, 143-4.
28. Ibid., 150.
29. Ibid., 153.
© 2011 Probe Ministries
 We can never get away from God. To some, this is quite threatening. To others, it is merely irritating or annoying. But for those who know and love God, it is deeply comforting and consoling, for it means that we are never alone.
We can never get away from God. To some, this is quite threatening. To others, it is merely irritating or annoying. But for those who know and love God, it is deeply comforting and consoling, for it means that we are never alone. During an eclipse, the heavens declare the glory of God by allowing us to see things about the sun we wouldn’t be able to observe any other way, beautiful and gloriously resplendent. Just before totality we can see “Baily’s Beads.” Only seen during an eclipse, bright “beads” appear at the edge of the moon where the sun is shining through lunar valleys, a feature of the moon’s rugged landscape. This is followed by the “diamond ring” effect, where the brightness of the sun radiates as a thin band around the circumference of the moon, and the last moments of the sun’s visibility explode like a diamond made of pure light. After the minutes of totality, the diamond ring effect appears again on the opposite side of the moon as the first rays of the sun flare brilliantly. These sky-jewelry phenomena are so outside of mankind’s control that witnessing them stirs our spirits (even on YouTube!) with the truth of Romans 1:20—”God’s invisible qualities—his eternal power and divine nature—have been clearly seen, being understood from what has been made, so that people are without excuse.”
During an eclipse, the heavens declare the glory of God by allowing us to see things about the sun we wouldn’t be able to observe any other way, beautiful and gloriously resplendent. Just before totality we can see “Baily’s Beads.” Only seen during an eclipse, bright “beads” appear at the edge of the moon where the sun is shining through lunar valleys, a feature of the moon’s rugged landscape. This is followed by the “diamond ring” effect, where the brightness of the sun radiates as a thin band around the circumference of the moon, and the last moments of the sun’s visibility explode like a diamond made of pure light. After the minutes of totality, the diamond ring effect appears again on the opposite side of the moon as the first rays of the sun flare brilliantly. These sky-jewelry phenomena are so outside of mankind’s control that witnessing them stirs our spirits (even on YouTube!) with the truth of Romans 1:20—”God’s invisible qualities—his eternal power and divine nature—have been clearly seen, being understood from what has been made, so that people are without excuse.” A total solar eclipse offers so much more, though, than Baily’s Beads and the Diamond Ring. At the moment of totality, the pinkish arc of the sun’s chromosphere (the part of the sun’s atmosphere just above the surface) suddenly “turns on” as if an unseen hand flips a switch. I knew God is very fond of pink because of how He paints glorious sunrises and sunsets in Earth’s skies, but those fortunate enough to see a total eclipse can see how He radiates pinkness from the sun itself! The heavens declare the glory of God!
A total solar eclipse offers so much more, though, than Baily’s Beads and the Diamond Ring. At the moment of totality, the pinkish arc of the sun’s chromosphere (the part of the sun’s atmosphere just above the surface) suddenly “turns on” as if an unseen hand flips a switch. I knew God is very fond of pink because of how He paints glorious sunrises and sunsets in Earth’s skies, but those fortunate enough to see a total eclipse can see how He radiates pinkness from the sun itself! The heavens declare the glory of God! For the few minutes of totality, the naked eye can see the sun’s lovely corona (Latin for crown) streaming out from the sun. We can’t see the corona except during an eclipse because looking straight at the sun for even a few seconds causes eye damage, and because the sun’s ball of fire overwhelms the (visually) fragile corona. This is another way that an eclipse allows us to see how the heavens declare the glory of God.
For the few minutes of totality, the naked eye can see the sun’s lovely corona (Latin for crown) streaming out from the sun. We can’t see the corona except during an eclipse because looking straight at the sun for even a few seconds causes eye damage, and because the sun’s ball of fire overwhelms the (visually) fragile corona. This is another way that an eclipse allows us to see how the heavens declare the glory of God. These are good questions and deserve to be asked. “Traditional” beliefs may not always be right, and at times they deserve to be reexamined. Bell then in the final pages of his preface implies that those who oppose his view are judgmental and not open to discussion of vital doctrines of the faith. This is part of his strategy to discourage any criticism of his position. However, Scripture calls us to evaluate all teachings and discern truth from error (1 Thess. 5:21; 1 Jn. 4:1).
These are good questions and deserve to be asked. “Traditional” beliefs may not always be right, and at times they deserve to be reexamined. Bell then in the final pages of his preface implies that those who oppose his view are judgmental and not open to discussion of vital doctrines of the faith. This is part of his strategy to discourage any criticism of his position. However, Scripture calls us to evaluate all teachings and discern truth from error (1 Thess. 5:21; 1 Jn. 4:1).

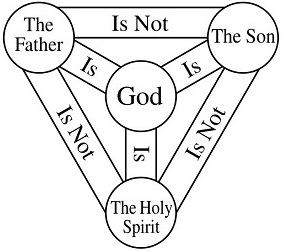 Even though it’s short, this definition is both a mouthful and a mind full. But let’s settle on four basic concepts before we move on to the implications. At the heart of the definition of the Blessed Trinity we have: one God, three Persons, who are coequal and coeternal. With this sketch in place, then, we are ready to move out and survey the importance of the Trinity with respect to the Christian worldview and its practical aspects for the Christian life. At the end of our discussion I truly hope that we can affirm together our love for the Trinity.
Even though it’s short, this definition is both a mouthful and a mind full. But let’s settle on four basic concepts before we move on to the implications. At the heart of the definition of the Blessed Trinity we have: one God, three Persons, who are coequal and coeternal. With this sketch in place, then, we are ready to move out and survey the importance of the Trinity with respect to the Christian worldview and its practical aspects for the Christian life. At the end of our discussion I truly hope that we can affirm together our love for the Trinity.