Steve Cable explores the results of Probe’s new 2020 survey, examining what people believe about Jesus in His time on earth, and His claim to be the only way to the Father.
Our 2020 survey reveals a striking decline in evangelical religious beliefs and practices over the last ten years. In our first article, we saw a significant degradation in the percentage of American young adults who are born again{1} and profess a biblically informed worldview{2}. Perhaps a biblical worldview, as defined by the set of questions we used, is not an accurate gauge of an orthodox Christian belief.
In this article, we will look at several other areas designed to identify those people who closely align their thoughts with the teaching of the Bible. We will look at two areas of belief for all American young adults and for Born Again Protestants in greater detail:
1. Do you believe in some critical aspects of Jesus Christ and His time on earth?
2. Do you believe that Jesus was right in saying “No one comes to the Father except by Me”?
We will look at these two areas alone and then see how those with a biblical worldview align with these questions.
Topic 1: What About Jesus and His Time on Earth?
In our survey, we asked three questions specifically about Jesus. The first question was about what caused Jesus to die on a cross as given below.
1. Why did Jesus die on a cross?
a. He threatened the Roman authorities’ control over Israel.
b. He threatened the stature of the Jewish leaders of the day.
c. To redeem us by taking our sins and our punishment upon Himself.
d. He never died on a cross.
e. He failed in his mission to convert the Jewish people into believers.
f. I don’t know.
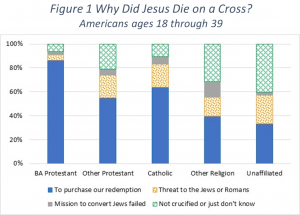 The responses for ages 18 through 39 are shown in Figure 1. As shown, Born Again Protestants have a far greater percentage, over 85%, stating that Jesus was crucified to purchase our redemption. One would suspect that all Protestant and Catholic leaders would want their people to know that Jesus’ death on the cross was for their redemption. Yet, less than two thirds of each group selected that answer. Note that the answer to this question did not say that salvation was through grace alone. So even those with a works-based gospel should still select that answer.
The responses for ages 18 through 39 are shown in Figure 1. As shown, Born Again Protestants have a far greater percentage, over 85%, stating that Jesus was crucified to purchase our redemption. One would suspect that all Protestant and Catholic leaders would want their people to know that Jesus’ death on the cross was for their redemption. Yet, less than two thirds of each group selected that answer. Note that the answer to this question did not say that salvation was through grace alone. So even those with a works-based gospel should still select that answer.
A fair number of Other Protestants and Catholics (about 20% of each group) said that either the Jewish leaders or the Romans caused Jesus’ death on the cross. But any Christian should realize that Jesus had to choose crucifixion. Prior attempts by authoritative groups demonstrated that they could not lay a hand on him otherwise.
Interestingly, about 40% of Other Religions and 30% of the Unaffiliated say Jesus died to redeem us. They understand this is what Christians say about Jesus’ crucifixion. It is the best answer for them because it doesn’t say that Jesus’ death actually worked to redeem us, only that He did
it to redeem us. Also note that roughly one third of the Other Religion category is made up of people who affiliate with Christian cults, e.g. Mormons and Jehovah’s Witnesses.
The second question is:
2. Jesus will return to this earth to save those who await His coming.
a. Answers ranging from Strongly Agree to Strongly Disagree.
This question is almost a quote of Hebrews 9:27-28 ESV, “And just as it is appointed for man to die once, and after that comes judgement, so Christ, having been offered once to bear the sins of many, will appear a second time, not to deal with sin but to save those who are eagerly waiting for him.” As you can see, this verse answers question 1 and question 2. The apostle Paul writing in 1 Thessalonians 4:16 says, “For the Lord himself will come down from heaven with a shout of command, with the voice of the archangel, and with the trumpet of God, and the dead in Christ will rise first.” He makes it clear that the Lord Jesus will return to the earth to call us to Himself.
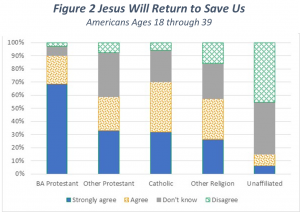 The results for this question follow a similar pattern to those for the first question above with a little less surety shown among Christians. As shown, just over two thirds of Born Again Protestants strongly agree that Jesus will return to save. Meaning that almost one third of them are not absolutely sure of Jesus’ return.
The results for this question follow a similar pattern to those for the first question above with a little less surety shown among Christians. As shown, just over two thirds of Born Again Protestants strongly agree that Jesus will return to save. Meaning that almost one third of them are not absolutely sure of Jesus’ return.
For other Christian groups, only about one third of them strongly agree with this statement. Almost one third say they Disagree or Don’t Know about this statement.
Once again, over half of those affiliated with Other Religions affirm what they believe to be taught by the Christian religion. At the same time, the Unaffiliated continue to show that very few of them affirm any Christian beliefs.
The third question (also used for determining a Basic Biblical Worldview) is:
3. When He lived on earth, Jesus committed sins like other people.
a. Answers ranging from Agree Strongly to Disagree Strongly
The Bible clearly states that Jesus lived a sinless life. For example, Hebrews 4:15 ESV states, “For we do not have a high priest who is unable to sympathize with our weaknesses, but one who in every respect has been tempted as we are, yet without sin.” And again in 2 Corinthians 5:21, “God made the one who did not know sin to be sin for us so that in Him we would become the righteousness of God.“ As indicated in this verse, God laid our sins upon Jesus in His earthly death. Jesus did not sin but He carried our sins to the cross and the grave to redeem us. If Jesus were a sinner like you and me, His death would have been for His own sin rather than for the sins of the world.
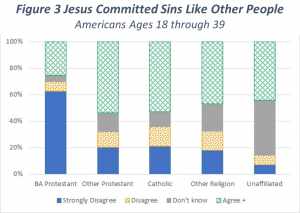 Young adult American beliefs about this statement follow a similar pattern as the first two questions. Once again, about one third of Born Again Protestants either Don’t Know or Agree with this statement. Having this large a number of Born Again Protestants who don’t accept a primary belief of Biblical Christianity is disappointing.
Young adult American beliefs about this statement follow a similar pattern as the first two questions. Once again, about one third of Born Again Protestants either Don’t Know or Agree with this statement. Having this large a number of Born Again Protestants who don’t accept a primary belief of Biblical Christianity is disappointing.
However, four out of five respondents who affiliated with Other Protestant or Catholic beliefs do not strongly believe that Jesus lived a sinless life. The Unaffiliated group continues to show their aversion to accepting any Christian religious doctrines.
Accepting a Doctrinally Consistent Set of Beliefs
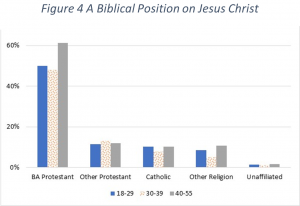 What happens when we look at how many Born Again Protestants take a biblically consistent view on all three of these questions? Consider the results shown in Figure 4. First, we see that young adult Born Again Protestants drop from about two thirds for the individual questions down to about one half when looking at all three questions. It appears that about one half of those categorized as Born Again Protestants are trusting Jesus to save them but do not have a good understanding of biblical teaching on Jesus.
What happens when we look at how many Born Again Protestants take a biblically consistent view on all three of these questions? Consider the results shown in Figure 4. First, we see that young adult Born Again Protestants drop from about two thirds for the individual questions down to about one half when looking at all three questions. It appears that about one half of those categorized as Born Again Protestants are trusting Jesus to save them but do not have a good understanding of biblical teaching on Jesus.
As you can see, all other religious groups drop to around one in ten or less with a good understanding of Jesus. The Unaffiliated drop to a level that is basically zero. In toto, about one out of six Americans age 55 and under have an understanding of who Jesus really is in these three fundamental areas.
Does Having a Basic Biblical Worldview Equate to Having a Biblical Understanding of Jesus?
For most people it does. Approximately 90% of people with a Basic Biblical Worldview have a biblical understanding of Jesus, i.e. answer the three Jesus questions from a biblical perspective. This finding (especially if true across other questions where many Born Again Christians ascribe to an unbiblical viewpoint) is important because the four simple questions which define a Basic Biblical Worldview identifies a set of people who also take a biblical view of Jesus’ purpose.
Topic 2: Are there multiple ways to heaven?
Pluralism is the belief that there are multiple ways to obtain a right relationship with God, including most if not all world religions. The Bible is very clear on how people can be reconciled to God and obtain eternal life. First, we cannot receive it through our own efforts at righteous living. This truth is addressed throughout the New Testament including Romans 3:23, “For there is no distinction, for all have sinned and fall short of the glory of God.” And Titus 3:5, “He saved us not by works of righteousness that we have done but on the basis of his mercy . . .”
Second, we cannot receive it by placing our faith in some other person or deity. If we try, we are still weighed down by our sin, and that other person or deity has no standing before the living God. Even an angel of the living God has no standing on which to intercede for our salvation as we
see in Hebrews 2:5, “For He did not put the world to come, about which we have been speaking, under the control of angels.”
The only way God could redeem us was through the sacrifice of Jesus, fully God and fully man. As Romans goes on to say in 3:24, “But they are justified freely by His grace through the redemption that is in Christ Jesus.” And Titus 3:5 continues, “[T]hrough the washing of the new birth and
the renewing of the Holy Spirit, whom he poured out on us in full measure through Jesus Christ our savior.”
Jesus clearly stated, “No one comes to the Father except through me.” The high price of degradation and suffering paid through Jesus’ life and death excludes the possibility of Jesus being just one of several options offered by God.
What do Americans believe about multiple ways to heaven? And, especially what do Born Again Christians believe? To determine who was a pluralist, we asked what the respondents thought about the following two statements:
1. Muhammad, Buddha and Jesus all taught valid ways to God. Answers from Disagree Strongly to Agree Strongly
2. I believe that the only way to a true relationship with God is through Jesus Christ. Answers from Disagree Strongly to Agree Strongly
Who Believes in Multiple Ways to God
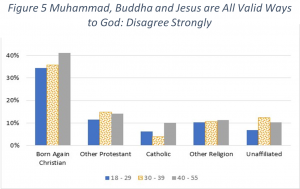 First let’s look at just question number one across the various religious groups, looking for the answer Disagree strongly as shown in Figure 5{3}. If someone disagrees with this statement, they could be a Christian or a Muslim or a Buddhist, etc. The first thing you may notice is that all religious groups other than Born Again Christian all congregate around 5% to 15%. So, for all these groups, around one in ten people take a strong non-pluralistic view. Or turning it around, about 9 out of 10 of them are pluralists.
First let’s look at just question number one across the various religious groups, looking for the answer Disagree strongly as shown in Figure 5{3}. If someone disagrees with this statement, they could be a Christian or a Muslim or a Buddhist, etc. The first thing you may notice is that all religious groups other than Born Again Christian all congregate around 5% to 15%. So, for all these groups, around one in ten people take a strong non-pluralistic view. Or turning it around, about 9 out of 10 of them are pluralists.
The real shocker jumping from this page is that over 60% of Born Again Christians are also pluralists. Apparently, a majority of Born Again Christians are ignorant about the basic teachings of their faith. Also, it is interesting and disturbing that the percentage of Born Again Christians who are not pluralistic is almost flat across the ages from 18 to 55. A strong majority of Born Again Christians are pluralists across that entire age range.
Who Believes Jesus is the Only Way
Now to narrow the question even further, we could have stated “Only Jesus taught valid ways to God.” The percentage of people strongly agreeing with this statement should be a subset of the people who disagreed strongly with the question above, “Muhammad, Buddha and Jesus all taught valid ways to God.”
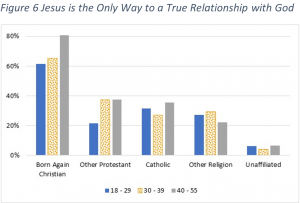 Instead, we asked this second question in a slightly different way but with the same intent: “I believe that the only way to a true relationship with God is through Jesus Christ.” We thought that this question would be
Instead, we asked this second question in a slightly different way but with the same intent: “I believe that the only way to a true relationship with God is through Jesus Christ.” We thought that this question would be
equivalent to the first one in the prior paragraph. But as we will see, people’s brains allow them to give answers that contradict each other.
Comparing this chart with the prior one, we see that Born Again Christians are at least 25 percentage points higher for this second question. And, the other Christian religious groups are higher by about 25 percentage points as well. And even Other Religions are up by over ten percentage points. Only the Unaffiliated drop from the first question to the second, dropping by almost half from ten percentage points down to about five percentage points.
An Inconsistent Worldview Among Many Born Again Christians
The results outlined above are disconcerting in that if the answers to the two questions were consistent, we would see Figure 6 reporting lower numbers than Figure 5 which is clearly not the case. Logically, one could say that Mohammad, Buddha, and Jesus are not all valid ways to God while still saying that Jesus is not the only way to God. You could believe, for example, that Buddha is the only one who taught a valid way to God. But, if you say that Jesus is the only way to a true relationship with God, then it follows that you believe that Mohammad, Buddha, and Jesus cannot all be valid ways to God.
 However, the survey respondents show us that one does not have to give answers which logically support one another. Even if some of the respondents misread the statement, the difference between the two is great enough that it is safe to assume that the results are not primarily attributable to misreading.
However, the survey respondents show us that one does not have to give answers which logically support one another. Even if some of the respondents misread the statement, the difference between the two is great enough that it is safe to assume that the results are not primarily attributable to misreading.
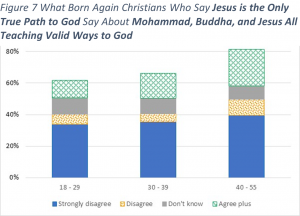
In Figure 7, we look at what the Born Again Christians who stated that Jesus is the only way to a true relationship with God said when responding to the question about Mohammad, Buddha and Jesus. First note that the total height of each column is the same as the Born Again Christian columns in Figure 6. As shown, almost half of each column represents those who did not strongly disagree with the pluralistic view. For the youngest adults, that upper portion is about evenly split between those who Don’t Know and those who Agree or Strongly Agree that the three men taught valid ways to God. For those ages 40 through 55, we see that a significantly higher percentage affirm that all three men taught valid ways to God.
Based on these results, about one third of Born Again Christians appear to have a consistent biblical view toward pluralism. Another third appear to be totally in line with the pluralist position. The last third are those who want to say that Jesus is the only true path to God AND that Mohammad and Buddha also taught valid ways to God. In church, they may say that Jesus in the only way, but out in the world they act as if Muslims and Buddhists don’t need to know this critical truth. These individuals have an incoherent worldview.
Changes over the Last Decade
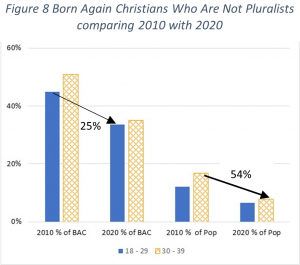 How have the statistics on Born Again Christians and pluralism changed from 2010 to 2020? As shown in the figure, we see a significant drop in the percent of BACs who are not pluralists. Those age 18 to 29 drop by 25% (from 45% to 34% of all BACs) and those age 30 to 39 drop by 31% (from 51% to 35% of all BACs).
How have the statistics on Born Again Christians and pluralism changed from 2010 to 2020? As shown in the figure, we see a significant drop in the percent of BACs who are not pluralists. Those age 18 to 29 drop by 25% (from 45% to 34% of all BACs) and those age 30 to 39 drop by 31% (from 51% to 35% of all BACs).
Of course, we need to remember that the percentage of BACs in the population has dropped as well. So, when we look at the percentage of Born Again Christians who are definitely not pluralists in our country the drop off is greater. As shown the number of those age 30 to 39 drops from 17% in 2010 to less than half of that number at 8% in 2020 (a drop of 54%).
Over the last decade, Born Again Christians in America have continued to grow in the number who are pluralists.
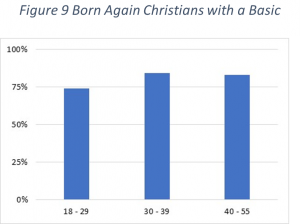 What about that smaller subset of people who have a Basic Biblical Worldview? Do a majority of them also have a pluralistic worldview? The answer is no. As shown, between 75% and 85% of them are not pluralists.
What about that smaller subset of people who have a Basic Biblical Worldview? Do a majority of them also have a pluralistic worldview? The answer is no. As shown, between 75% and 85% of them are not pluralists.
This result is not a surprise since the Basic Biblical Worldview questions do not align well with a pluralistic view. However, the result that about one in four of Born Again Christians with a Basic Biblical Worldview appear to be pluralists is unsettling.
Countering the Negative Slide
If you are reading this, you may want to do something to help reverse this trend among Born Again Christians to misunderstand who Jesus is and His unique ability to redeem us and restore into a relationship with our Creator. Here a several suggestions that can help in this reversal.
Faithful prayer. Daily pray for the lost and against the forces of darkness so visibly arrayed against them. Pray for the saved, that they may take up the true gospel and cling to the eternal truth of Jesus.
Preach, teach and speak OFTEN about the events of the cross and the tomb.
• Explain that only someone perfectly sinless could undertake the task of reconciling us before a holy God. Make sure they understand that “God made him who knew no sin to be sin on our behalf in order that we may become the righteousness of God in him.” 2 Corinthians 5:21
• Explain that only God, in the person of Jesus Christ, could be that sinless sacrifice. God had to undergo the pain and suffering of separating Himself from His Son on the cross. “Though he existed in the form of God, he did not regard equality with God as something to be grasped, but emptied himself by taking on the form of a slave, by looking like other men, and by sharing in human nature. He humbled himself by becoming obedient to the point of death—even death on a cross!” Philippians 2:6-8
• Explain that the cost was so high, no other way to God is possible for sinful man. No one can come to the Father except through the Son and anyone may come through Him. “God desires all men to be saved and to come to the knowledge of the truth. For there is one God and one intermediary between God and humanity, Christ Jesus, himself human, who gave himself as a ransom for all, revealing God’s purpose at his appointed time.” 1 Timothy 2:4-6
• Explain that Jesus’ return is delayed only by the loving patience of God who is waiting for all to come to Jesus who will. “The Lord is not slow concerning his promise, as some regard slowness, but is being patient toward you because he does not wish for any to perish but for all to come to repentance.” 2 Peter 3:9
• Explain that accepting pluralism will not automatically get your non-Christian friends into heaven. Only the truth of Christ presented to them by willing lips has the power to change their eternal destiny. If you care about them, you will share with them.
It is critical that every teenager, young adult, and older adult who crosses our path needs to have these truths reiterated for them. Use different techniques and different word pictures as you strive by the power of the Holy Spirit to continually make this message clear. We know God desires to work in their life.
Notes
1. A Born Again person in our survey results is someone who 1) has made a personal commitment to Jesus Christ that is still important in their life today and 2) when asked what will happen to you after you die, they answer I will go to heaven because I confessed my sins and accepted Jesus Christ as my savior.
2. See our first article: Introducing Probe’s New Survey: Religious Views and Practices 2020 for a description of the biblical worldview questions used.
3. Born Again Christians include Catholics who answered the born again questions to allow comparison with the 2010 survey, but in the Catholic category we include all Catholics including those who are born again. About 20% of Catholics affirm the two born again questions.